During the development of the Weather project, we continuously submitted new changes. While some updates worked as expected, others introduced bugs. Ensuring high code quality is essential to maintaining the reliability and availability of the product. To minimize bugs and maintain stability, it’s crucial to focus on testing. In this blog, I’ll introduce the main testing methods used in the industry and explain how we’ve implemented them in our project.
Best practices
In today’s fast-paced software industry, quality is no longer treated as a final checkpoint at the end of development. Instead, it has become an essential part of the entire lifecycle. Leading teams are adopting a quality-first mindset, embedding testing and validation from the earliest stages of coding. This shift aligns with a broader industry movement toward automation, continuous feedback, and empowered development teams. Rather than depending solely on post-development QA, modern engineering emphasizes proactive strategies such as early testing, modular validation, and real-time integration checks. These practices help reduce the cost and complexity of fixing defects, while also promoting a culture of accountability and building confidence in delivering reliable software at scale.
Shift-Left Testing
Testing is becoming a continuous and proactive process nowadays. Shift-left testing brings quality assurance into the earliest phases of the software lifecycle. By validating code as soon as it is written, teams can detect and address issues early, before they become complex and costly. This approach enables faster feedback, fewer late-stage bugs, and greater developer confidence.
Continuous Integration (CI)
In fast-paced development environments, continuous integration provides the stability needed to maintain momentum. Every time code is submitted, automated tests run to verify that new changes work correctly and integrate well with the existing codebase. CI helps ensure that the application remains functional and reliable across different environments, supporting rapid development without compromising quality.
Unit Testing
Unit testing strengthens the foundation of any software project. By verifying the behavior of individual functions or components in isolation, developers can prevent bugs and better understand the intended functionality. Well-written unit tests make the codebase more reliable and easier to maintain, especially when introducing new features or refactoring existing code.
Static Code Analysis (Linting)
Maintaining high code quality starts with consistency and attention to detail. Linting tools automatically review source code to detect syntax errors, style violations, and potential bugs without running the code. By enforcing coding standards and identifying issues early, linting improves readability, reduces technical debt, and supports a clean and maintainable codebase that the whole team can work with more effectively.
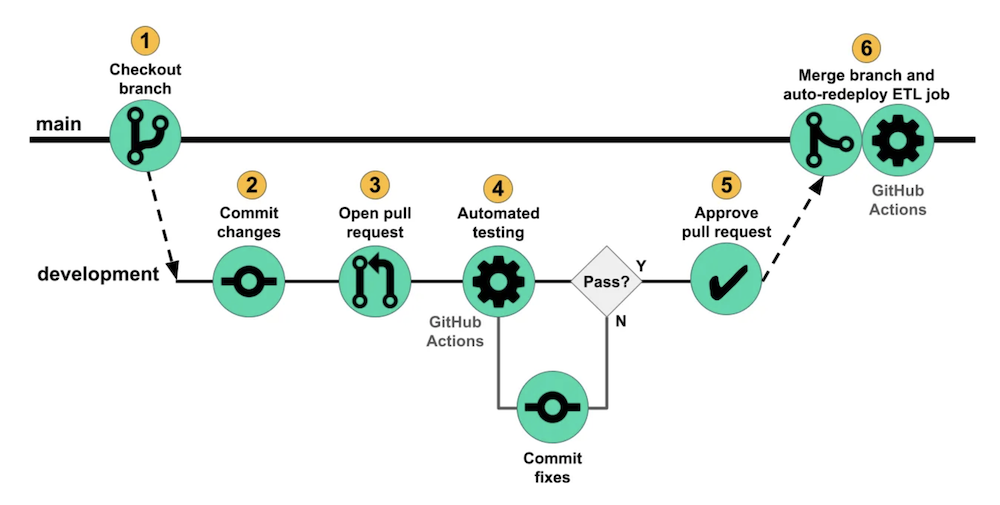
Github Actions
GitHub Actions allows the definition of workflows that run automatically when specific events occur in a repository. These workflows can install dependencies, run tests, lint code, and deploy to servers or cloud platforms. GitHub Actions offers numerous benefits:
- Easy to integrate – Works seamlessly with GitHub repositories.
- Automates repetitive tasks – Saves time and reduces human error.
- Enforces testing – Automatically runs tests on every commit or pull request.
- Prevents broken code from being merged – Only clean, tested code goes into main.
- Improves visibility – Clear logs and status checks help track down issues fast.
Implementation
To enable CI for our project, we created a GitHub Actions workflow that includes Pylint and Pytest for code quality checks and unit testing.
+------------------------+
| Developer pushes code |
| (git push / PR) |
+-----------+------------+
|
v
+----------------------------+
| GitHub Actions is triggered |
| on: push / pull_request |
+-----------+----------------+
|
v
+----------------------------+
| Checkout source code |
| actions/checkout@v4 |
+-----------+----------------+
|
v
+----------------------------+
| Set up Python environment |
| actions/setup-python |
+-----------+----------------+
|
v
+-----------------------------------------+
| Install dependencies |
| pip install -r requirements.txt |
+-----------+-----------------------------+
|
v
+----------------------------+
| Run pylint (code quality) |
| pylint package/ |
+-----------+----------------+
|
v
+----------------------------+
| Run pytest (unit tests) |
| pytest tests/ |
+----------------------------+Some findings and thoughts
- Implementing automated testing and continuous integration helped us detect bugs early and maintain high code quality throughout the development process.
- Integrating linting tools like pylint into our CI pipeline significantly improved code consistency and reduced the time spent on manual code reviews.